ArgoCD: GitOps per Kubernetes - Guida Completa 2026
ArgoCD e diventato lo standard de facto per implementare GitOps su Kubernetes. Con oltre 15.000 stelle su GitHub e l'adozione da parte di aziende come Intuit, Red Hat e Tesla, ArgoCD rappresenta la soluzione piu matura per il continuous deployment dichiarativo. In questa guida vedremo come installare, configurare e utilizzare ArgoCD per automatizzare i deployment delle tue applicazioni Kubernetes.
Cos'e GitOps
Prima di ArgoCD, capiamo il paradigma GitOps.
Principi GitOps
- Dichiarativo: L'intero sistema e descritto in modo dichiarativo
- Versioned: Lo stato desiderato e versionato in Git
- Automatico: Le modifiche approvate sono applicate automaticamente
- Riconciliazione continua: Il sistema corregge automaticamente le derive
GitOps vs CI/CD Tradizionale
CI/CD Tradizionale (Push-based):
Developer -> Git -> CI Pipeline -> kubectl apply -> ClusterProblemi:
- CI ha accesso al cluster (sicurezza)
- Nessun audit trail completo
- Difficile rollback
GitOps (Pull-based):
Developer -> Git <- ArgoCD (nel cluster) -> RiconciliazioneVantaggi:
- Il cluster "tira" le configurazioni
- Git e l'unica fonte di verita
- Audit trail completo
- Rollback = git revert
Cos'e ArgoCD
ArgoCD e un controller Kubernetes che:
- Monitora repository Git
- Confronta stato desiderato (Git) vs stato attuale (cluster)
- Sincronizza automaticamente le differenze
- Fornisce UI e CLI per gestione
Architettura
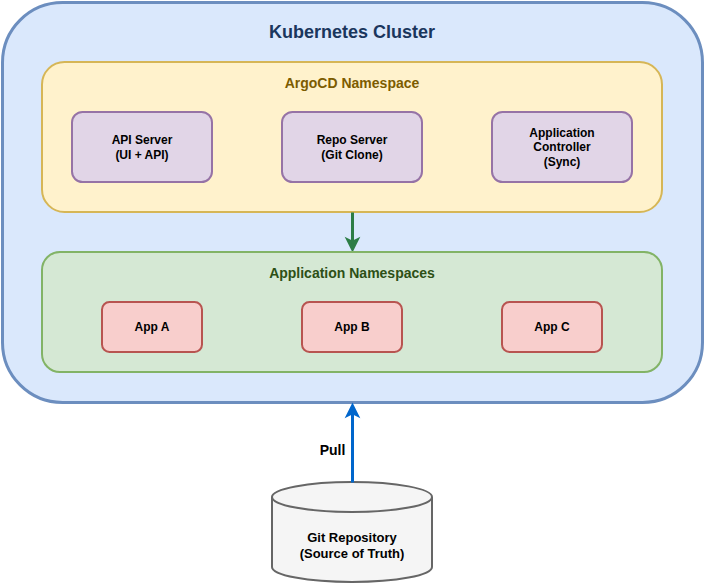
Componenti Principali
| Componente | Funzione |
|---|---|
| API Server | Espone API REST e gRPC, serve la UI |
| Repository Server | Clona e cache dei repository Git |
| Application Controller | Monitora e sincronizza le applicazioni |
| Redis | Cache per lo stato delle applicazioni |
| Dex | Identity provider per SSO (opzionale) |
Installazione
Prerequisiti
- Kubernetes cluster (1.25+)
- kubectl configurato
- Helm 3 (opzionale ma consigliato)
Metodo 1: Manifest YAML (Semplice)
# Crea namespace
kubectl create namespace argocd
# Installa ArgoCD
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
# Verifica pods
kubectl get pods -n argocdMetodo 2: Helm (Consigliato per produzione)
# Aggiungi repo Helm
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm repo update
# Installa con valori custom
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd \
--namespace argocd \
--create-namespace \
--values values.yamlvalues.yaml esempio:
server:
replicas: 2
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
hosts:
- argocd.example.com
tls:
- secretName: argocd-tls
hosts:
- argocd.example.com
controller:
replicas: 1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
repoServer:
replicas: 2
redis:
enabled: true
configs:
params:
server.insecure: false
cm:
url: https://argocd.example.comAccesso Iniziale
# Password admin iniziale
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret \
-o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
# Port forward per accesso locale
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
# Accedi a https://localhost:8080
# Username: admin
# Password: (quella ottenuta sopra)Installare CLI
# Linux
curl -sSL -o argocd https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64
chmod +x argocd
sudo mv argocd /usr/local/bin/
# macOS
brew install argocd
# Login CLI
argocd login localhost:8080Concetti Fondamentali
Application
Una Application in ArgoCD definisce:
- Source: dove sono i manifest (Git repo)
- Destination: dove deployare (cluster + namespace)
- Sync policy: come sincronizzare
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/myorg/my-app.git
targetRevision: main
path: kubernetes/
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: my-app
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=trueProject
Un AppProject raggruppa applicazioni con policy comuni:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: AppProject
metadata:
name: production
namespace: argocd
spec:
description: Production applications
sourceRepos:
- https://github.com/myorg/*
destinations:
- namespace: '*'
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: ''
kind: Namespace
roles:
- name: developer
policies:
- p, proj:production:developer, applications, get, production/*, allow
- p, proj:production:developer, applications, sync, production/*, allowRepository
Registra repository Git privati:
# Via CLI
argocd repo add https://github.com/myorg/private-repo.git \
--username git \
--password $GITHUB_TOKENSync Policies e Strategie
Auto Sync
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true # Elimina risorse non in Git
selfHeal: true # Correggi modifiche manuali
allowEmpty: false # Non sync se repo vuotoSync Options
syncOptions:
- Validate=true # Valida manifest prima di sync
- CreateNamespace=true # Crea namespace se non esiste
- PrunePropagationPolicy=foreground # Attendi eliminazione
- PruneLast=true # Prune dopo apply
- ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=true # Apply solo risorse OutOfSync
- ServerSideApply=true # Usa server-side applySync Waves e Hooks
Controlla l'ordine di deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: database
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-1" # Prima
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: backend
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "0" # Dopo database
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: frontend
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "1" # Dopo backendResource Hooks
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: db-migration
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PreSync
argocd.argoproj.io/hook-delete-policy: HookSucceeded
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: migrate
image: myorg/migrations:latest
command: ["./migrate.sh"]
restartPolicy: NeverHook types:
PreSync: Prima della sincronizzazioneSync: Durante la sincronizzazionePostSync: Dopo la sincronizzazioneSyncFail: Se sync fallisce
Integrazione con Helm
ArgoCD supporta nativamente Helm charts:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
source:
repoURL: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
chart: ingress-nginx
targetRevision: 4.8.3
helm:
releaseName: nginx-ingress
values: |
controller:
replicaCount: 2
service:
type: LoadBalancer
metrics:
enabled: true
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: ingress-nginxApp of Apps Pattern
Gestisci tutte le applicazioni con una singola Application:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: root-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/myorg/argocd-apps.git
path: apps
targetRevision: main
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: argocd
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueNotifications
Configura notifiche per eventi:
# ConfigMap per notifiche
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-notifications-cm
data:
service.slack: |
token: $slack-token
template.app-sync-succeeded: |
message: |
Application {{.app.metadata.name}} sync succeeded.
Revision: {{.app.status.sync.revision}}
trigger.on-sync-succeeded: |
- when: app.status.sync.status == 'Synced'
send: [app-sync-succeeded]Best Practices Produzione
Sicurezza
# RBAC granulare
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-rbac-cm
namespace: argocd
data:
policy.csv: |
p, role:developer, applications, get, */*, allow
p, role:developer, applications, sync, */*, allow
p, role:admin, applications, *, */*, allow
g, developers, role:developer
g, admins, role:admin
policy.default: role:readonlyHigh Availability
# values.yaml per HA
controller:
replicas: 2
env:
- name: ARGOCD_CONTROLLER_REPLICAS
value: "2"
server:
replicas: 3
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 5
repoServer:
replicas: 3
autoscaling:
enabled: true
redis-ha:
enabled: trueTroubleshooting
Comandi Utili
# Stato applicazione
argocd app get my-app
# Log sync
argocd app logs my-app
# Force sync
argocd app sync my-app --force
# Diff
argocd app diff my-app
# History
argocd app history my-app
# Rollback
argocd app rollback my-app <revision>Problemi Comuni
App bloccata in "Progressing":
# Verifica risorse
kubectl get all -n my-app-namespace
# Eventi
kubectl get events -n my-app-namespace --sort-by='.lastTimestamp'Sync fallito:
# Dettagli errore
argocd app get my-app --show-operation
# Rimuovi risorse orfane
argocd app sync my-app --pruneConclusioni
ArgoCD e lo strumento essenziale per implementare GitOps su Kubernetes. Vantaggi chiave:
- Git come fonte di verita: audit trail completo
- Riconciliazione automatica: il cluster si auto-corregge
- UI intuitiva: visibilita immediata sullo stato
- Ecosistema maturo: integrazioni, plugin, community attiva
Checklist implementazione:
- Installa ArgoCD con Helm
- Configura SSO/RBAC
- Struttura repository GitOps
- Implementa App of Apps pattern
- Configura notifiche
- Testa rollback
- Documenta workflow team