ArgoCD: GitOps for Kubernetes - Complete Guide 2026
ArgoCD has become the de facto standard for implementing GitOps on Kubernetes. With over 15,000 stars on GitHub and adoption by companies like Intuit, Red Hat, and Tesla, ArgoCD represents the most mature solution for declarative continuous deployment. In this guide, we'll see how to install, configure, and use ArgoCD to automate deployments of your Kubernetes applications.
What is GitOps
Before diving into ArgoCD, let's understand the GitOps paradigm.
GitOps Principles
- Declarative: The entire system is described declaratively
- Versioned: The desired state is versioned in Git
- Automatic: Approved changes are applied automatically
- Continuous Reconciliation: The system automatically corrects drift
GitOps vs Traditional CI/CD
Traditional CI/CD (Push-based):
Developer -> Git -> CI Pipeline -> kubectl apply -> ClusterProblems:
- CI has access to the cluster (security concern)
- No complete audit trail
- Difficult rollback
GitOps (Pull-based):
Developer -> Git <- ArgoCD (in cluster) -> ReconciliationAdvantages:
- The cluster "pulls" configurations
- Git is the single source of truth
- Complete audit trail
- Rollback = git revert
What is ArgoCD
ArgoCD is a Kubernetes controller that:
- Monitors Git repositories
- Compares desired state (Git) vs actual state (cluster)
- Automatically synchronizes differences
- Provides UI and CLI for management
Architecture
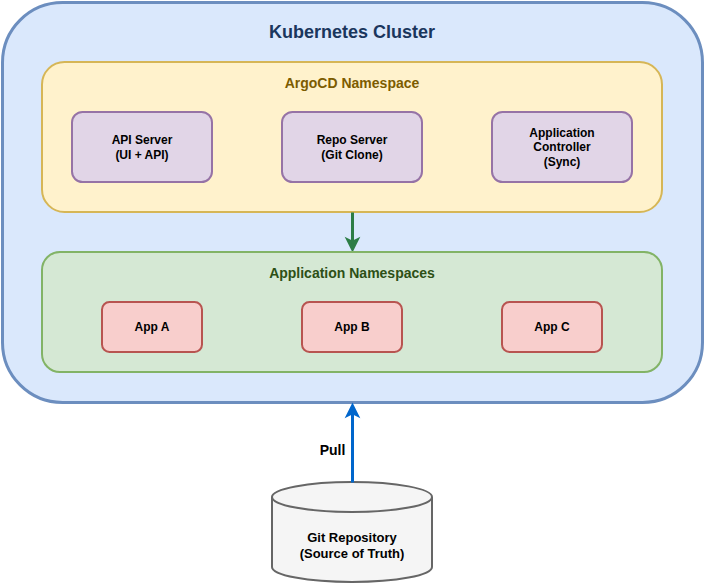
Main Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| API Server | Exposes REST and gRPC API, serves the UI |
| Repository Server | Clones and caches Git repositories |
| Application Controller | Monitors and synchronizes applications |
| Redis | Cache for application state |
| Dex | Identity provider for SSO (optional) |
Installation
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes cluster (1.25+)
- kubectl configured
- Helm 3 (optional but recommended)
Method 1: YAML Manifest (Simple)
# Create namespace
kubectl create namespace argocd
# Install ArgoCD
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
# Verify pods
kubectl get pods -n argocdMethod 2: Helm (Recommended for production)
# Add Helm repo
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm repo update
# Install with custom values
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd \
--namespace argocd \
--create-namespace \
--values values.yamlvalues.yaml example:
server:
replicas: 2
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: nginx
hosts:
- argocd.example.com
tls:
- secretName: argocd-tls
hosts:
- argocd.example.com
controller:
replicas: 1
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
repoServer:
replicas: 2
redis:
enabled: true
configs:
params:
server.insecure: false
cm:
url: https://argocd.example.comInitial Access
# Get initial admin password
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret \
-o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
# Port forward for local access
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
# Access https://localhost:8080
# Username: admin
# Password: (the one obtained above)Install CLI
# Linux
curl -sSL -o argocd https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64
chmod +x argocd
sudo mv argocd /usr/local/bin/
# macOS
brew install argocd
# CLI Login
argocd login localhost:8080Fundamental Concepts
Application
An Application in ArgoCD defines:
- Source: where manifests are located (Git repo)
- Destination: where to deploy (cluster + namespace)
- Sync policy: how to synchronize
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/myorg/my-app.git
targetRevision: main
path: kubernetes/
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: my-app
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=trueProject
An AppProject groups applications with common policies:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: AppProject
metadata:
name: production
namespace: argocd
spec:
description: Production applications
sourceRepos:
- https://github.com/myorg/*
destinations:
- namespace: '*'
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: ''
kind: Namespace
roles:
- name: developer
policies:
- p, proj:production:developer, applications, get, production/*, allow
- p, proj:production:developer, applications, sync, production/*, allowRepository
Register private Git repositories:
# Via CLI
argocd repo add https://github.com/myorg/private-repo.git \
--username git \
--password $GITHUB_TOKENSync Policies and Strategies
Auto Sync
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true # Delete resources not in Git
selfHeal: true # Correct manual changes
allowEmpty: false # Don't sync if repo is emptySync Options
syncOptions:
- Validate=true # Validate manifests before sync
- CreateNamespace=true # Create namespace if it doesn't exist
- PrunePropagationPolicy=foreground # Wait for deletion
- PruneLast=true # Prune after apply
- ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=true # Apply only OutOfSync resources
- ServerSideApply=true # Use server-side applySync Waves and Hooks
Control deployment order:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: database
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-1" # First
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: backend
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "0" # After database
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: frontend
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "1" # After backendResource Hooks
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: db-migration
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PreSync
argocd.argoproj.io/hook-delete-policy: HookSucceeded
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: migrate
image: myorg/migrations:latest
command: ["./migrate.sh"]
restartPolicy: NeverHook types:
PreSync: Before synchronizationSync: During synchronizationPostSync: After synchronizationSyncFail: If sync fails
Helm Integration
ArgoCD natively supports Helm charts:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
source:
repoURL: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
chart: ingress-nginx
targetRevision: 4.8.3
helm:
releaseName: nginx-ingress
values: |
controller:
replicaCount: 2
service:
type: LoadBalancer
metrics:
enabled: true
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: ingress-nginxApp of Apps Pattern
Manage all applications with a single Application:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: root-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/myorg/argocd-apps.git
path: apps
targetRevision: main
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: argocd
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueNotifications
Configure notifications for events:
# ConfigMap for notifications
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-notifications-cm
data:
service.slack: |
token: $slack-token
template.app-sync-succeeded: |
message: |
Application {{.app.metadata.name}} sync succeeded.
Revision: {{.app.status.sync.revision}}
trigger.on-sync-succeeded: |
- when: app.status.sync.status == 'Synced'
send: [app-sync-succeeded]Production Best Practices
Security
# Granular RBAC
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-rbac-cm
namespace: argocd
data:
policy.csv: |
p, role:developer, applications, get, */*, allow
p, role:developer, applications, sync, */*, allow
p, role:admin, applications, *, */*, allow
g, developers, role:developer
g, admins, role:admin
policy.default: role:readonlyHigh Availability
# values.yaml for HA
controller:
replicas: 2
env:
- name: ARGOCD_CONTROLLER_REPLICAS
value: "2"
server:
replicas: 3
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 5
repoServer:
replicas: 3
autoscaling:
enabled: true
redis-ha:
enabled: trueTroubleshooting
Useful Commands
# Application status
argocd app get my-app
# Sync logs
argocd app logs my-app
# Force sync
argocd app sync my-app --force
# Diff
argocd app diff my-app
# History
argocd app history my-app
# Rollback
argocd app rollback my-app <revision>Common Problems
App stuck in "Progressing":
# Check resources
kubectl get all -n my-app-namespace
# Events
kubectl get events -n my-app-namespace --sort-by='.lastTimestamp'Sync failed:
# Error details
argocd app get my-app --show-operation
# Remove orphan resources
argocd app sync my-app --pruneConclusions
ArgoCD is the essential tool for implementing GitOps on Kubernetes. Key advantages:
- Git as source of truth: complete audit trail
- Automatic reconciliation: the cluster self-corrects
- Intuitive UI: immediate visibility on state
- Mature ecosystem: integrations, plugins, active community
Implementation checklist:
- Install ArgoCD with Helm
- Configure SSO/RBAC
- Structure GitOps repository
- Implement App of Apps pattern
- Configure notifications
- Test rollback
- Document team workflow