Longhorn: Distributed Storage for Kubernetes - Complete Guide
Storage is one of the most complex problems in Kubernetes. Containers are ephemeral, but data must persist. Longhorn, a CNCF graduated project, solves this problem by offering distributed, resilient, and easy-to-manage storage. In this guide, we'll see how to install and configure Longhorn for your Kubernetes cluster.
The Storage Problem in Kubernetes
Ephemeral Storage
By default, Pod storage is ephemeral:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: my-app:latest
# Everything in /data is lost on restart!Traditional Solutions
| Solution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| hostPath | Simple | No portability, no HA |
| NFS | Shared | Single point of failure |
| Cloud Provider | Managed | Vendor lock-in, costs |
| Ceph | Powerful | High complexity |
| Longhorn | Simple + Distributed | Requires resources |
What is Longhorn
Longhorn is a distributed block storage system for Kubernetes that:
- Uses local node disks
- Replicates data across multiple nodes
- Manages snapshots and backups
- Provides integrated web UI
- Supports DR and migration
Architecture
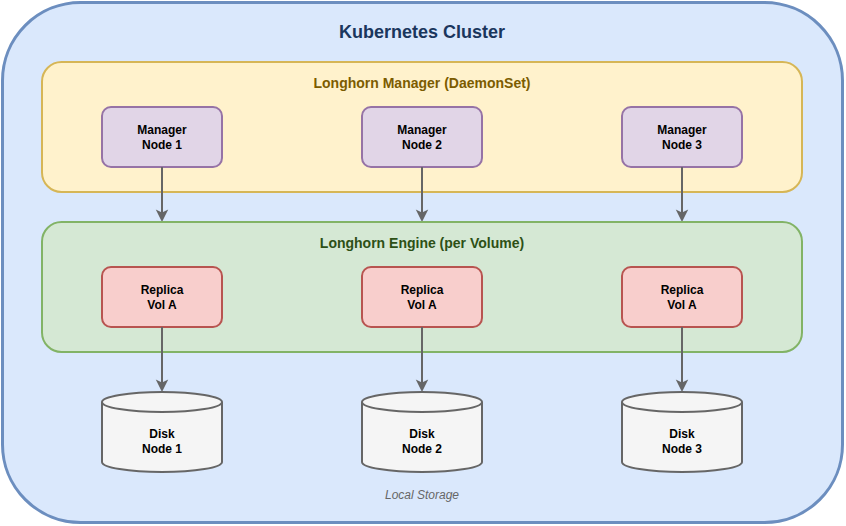
Main Components
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Longhorn Manager | Orchestration, API, UI |
| Longhorn Engine | iSCSI target, manages replicas |
| Replica | Data copy on local disk |
| CSI Driver | Kubernetes integration |
Requirements
Hardware
| Resource | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 3 | 3+ |
| CPU per node | 2 cores | 4+ cores |
| RAM per node | 4 GB | 8+ GB |
| Disk | SSD 50 GB | SSD/NVMe 200+ GB |
Software
Kubernetes: 1.25+
OS: Ubuntu 20.04+, RHEL 8+, SLES 15+
Filesystem: ext4, XFSNode Prerequisites
# Each node must have open-iscsi
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install open-iscsi
sudo systemctl enable iscsid
sudo systemctl start iscsid
# RHEL/CentOS
sudo yum install iscsi-initiator-utils
sudo systemctl enable iscsid
sudo systemctl start iscsidInstallation
Method 1: Helm (Recommended)
# Add repo
helm repo add longhorn https://charts.longhorn.io
helm repo update
# Install
helm install longhorn longhorn/longhorn \
--namespace longhorn-system \
--create-namespace \
--set defaultSettings.defaultDataPath="/var/lib/longhorn" \
--set defaultSettings.defaultReplicaCount=3Method 2: Kubectl
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/longhorn/longhorn/v1.6.0/deploy/longhorn.yamlVerify Installation
# Check pods
kubectl -n longhorn-system get pods
# Expected output
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS
longhorn-manager-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0
longhorn-driver-deployer-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0
longhorn-ui-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0
engine-image-ei-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0
instance-manager-xxxxx 1/1 Running 0UI Access
# Port forward
kubectl -n longhorn-system port-forward svc/longhorn-frontend 8080:80
# Access http://localhost:8080StorageClass Configuration
Default StorageClass
Longhorn automatically creates a StorageClass:
kubectl get storageclass
# NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY
# longhorn (default) driver.longhorn.io DeleteCustom StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: longhorn-ssd
provisioner: driver.longhorn.io
allowVolumeExpansion: true
reclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
parameters:
numberOfReplicas: "3"
staleReplicaTimeout: "2880"
fromBackup: ""
fsType: "ext4"
dataLocality: "best-effort"Important Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
numberOfReplicas | Number of replicas | 3 |
dataLocality | Data locality (disabled, best-effort, strict-local) | disabled |
diskSelector | Select specific disks | - |
nodeSelector | Select specific nodes | - |
Creating and Using Volumes
PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: longhorn
resources:
requests:
storage: 10GiUsing the Volume in a Pod
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-app
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: my-app:latest
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-dataStatefulSet with Longhorn
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: postgres
spec:
serviceName: postgres
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: postgres
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: postgres
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres:15
env:
- name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
value: "password"
- name: PGDATA
value: /var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: data
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
storageClassName: longhorn
resources:
requests:
storage: 20GiBackup and Disaster Recovery
Configure Backup Target
Longhorn supports backup to S3 or NFS.
S3 Backup:
# Secret for S3 credentials
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: s3-secret
namespace: longhorn-system
type: Opaque
stringData:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: "your-access-key"
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: "your-secret-key"# Configure via UI or CLI
# Settings > Backup Target
# s3://bucket-name@region/pathNFS Backup:
nfs://server-ip:/path/to/backupCreate Manual Backup
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: Backup
metadata:
name: my-data-backup
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
snapshotName: my-data-snapshot
labels:
app: my-app
type: manualRecurring Backups
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: RecurringJob
metadata:
name: daily-backup
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
cron: "0 2 * * *" # Every day at 2:00 AM
task: backup
retain: 7
concurrency: 1
groups:
- defaultRestore from Backup
1. Via UI: Volumes > Create Volume > From Backup
2. Via PVC:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: restored-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: longhorn
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
dataSource:
name: my-data-backup
kind: Backup
apiGroup: longhorn.ioSnapshots
Create Snapshot
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: Snapshot
metadata:
name: my-data-snap-1
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
volume: my-data
labels:
app: my-appRecurring Snapshots
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: RecurringJob
metadata:
name: hourly-snapshot
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
cron: "0 * * * *" # Every hour
task: snapshot
retain: 24 # Keep last 24
concurrency: 2
groups:
- defaultMonitoring
Prometheus Metrics
Longhorn exposes Prometheus metrics:
# ServiceMonitor for Prometheus Operator
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: longhorn
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: longhorn-manager
endpoints:
- port: managerMain Metrics
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
longhorn_volume_actual_size_bytes | Actual volume size |
longhorn_volume_capacity_bytes | Volume capacity |
longhorn_volume_state | Volume state |
longhorn_node_storage_capacity_bytes | Node storage capacity |
longhorn_node_storage_usage_bytes | Node storage usage |
Grafana Dashboard
Import dashboard ID: 13032 (Longhorn Dashboard)
Production Best Practices
Replica Count
# Minimum 3 replicas for HA
parameters:
numberOfReplicas: "3"Node Scheduling
Ensure replicas are distributed:
# Settings > Replica Node Level Soft Anti-Affinity: true
# Settings > Replica Zone Level Soft Anti-Affinity: trueDisk Scheduling
# Add tags to disks
kubectl -n longhorn-system label nodes node1 storage=ssdparameters:
diskSelector: "ssd"Backup Policy
# Daily backup with 7-day retention
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: RecurringJob
metadata:
name: daily-backup
spec:
cron: "0 3 * * *"
task: backup
retain: 7Troubleshooting
Volume Degraded
# Check volume status
kubectl -n longhorn-system get volumes.longhorn.io
# Details
kubectl -n longhorn-system describe volume my-volumeCommon causes:
- Node down
- Disk full
- Corrupted replica
Slow Replica Rebuild
# Increase concurrent rebuild
# Settings > Concurrent Replica Rebuild Per Node Limit: 5Insufficient Space
# Check space per node
kubectl -n longhorn-system get nodes.longhorn.io -o wideSolutions:
- Add disks
- Delete old snapshots
- Temporarily reduce replica count
Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Longhorn | Rook-Ceph | OpenEBS | Portworx |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low | High | Medium | Medium |
| Performance | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Integrated UI | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| S3 Backup | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| License | Apache 2.0 | Apache 2.0 | Apache 2.0 | Commercial |
| CNCF | Graduated | Graduated | Sandbox | No |
When to choose Longhorn:
- Small to medium clusters
- Teams with limited Kubernetes experience
- Need for quick setup
- Limited budget
Conclusions
Longhorn is the ideal solution for those looking for distributed storage on Kubernetes without the complexity of Ceph or the costs of enterprise solutions.
Implementation checklist:
- Node prerequisites (open-iscsi)
- Installation via Helm
- StorageClass configuration
- Backup target setup (S3/NFS)
- Recurring backup configured
- Active monitoring
- Restore testing